September 08, 2020
One of Your Body’s Best Kept Secrets...
The human body is fascinating – how systems are so interconnected. Each relying on the other to assess, react and act in order for us to eat, breath, move, think…and live! One of your body’s best kept secrets – mainly due to its recent discovery - is the Endocannabinoid System or ECS.
The ECS is a complex cell-signaling system that was identified in 1988 by researchers Allyn Howlett and William Devane at Saint Louis University School of Medicine in a government-controlled study. They were exploring THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol), a well-known cannabinoid found in cannabis when they found that we have cannabinoid receptors that respond to cannabis and these cannabinoid receptors are the most prevalent type of neurotransmitter receptor in our brain!
Today, experts are still trying to fully understand the ECS. We know it plays a role in regulating a range of functions and processes. To better understand the ECS system, let’s take a look at the root of its name. Endo is short for endogenous, meaning produced naturally inside the body, and cannabinoid derives from the Latin cannabis. So, endocannabinoid simply means cannabis-like substances that naturally occur in the body. The ECS exists and is active in your body even if you don’t use cannabis.
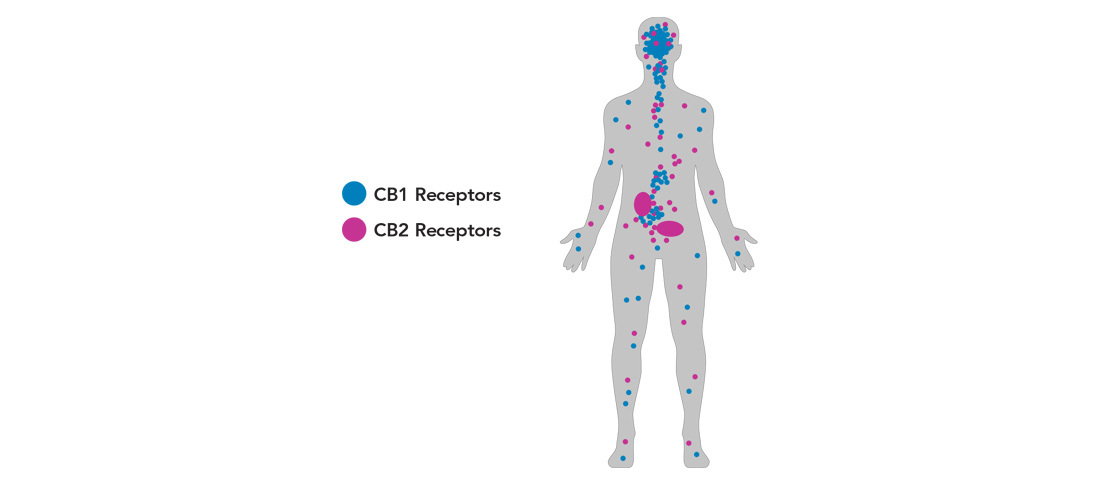
The ECS involves three core components: endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes.
Endocannabinoids are molecules similar to cannabinoids, but they’re produced by your body. These help keep internal functions running smoothly. Your body produces them as needed, making it difficult to know what typical levels are for each. They bind to endocannabinoid receptors signaling the ECS to take action. Once they carry out their job, enzymes break them down.
Your endocannabinoid system is crucial for your body to achieve “balance”.
Your ECS’s job is to keep your internal environment stable and optimal no matter what's going on in the environment around you. When something is operating outside of the right range, your body activates the ECS to help correct it.
So, when you're really hot and begin to sweat, thank your ECS for working to cool you down.
Stomach growling? That's your ECS helping remind you to eat because you need fuel.
The ECS uses cannabinoid receptors found in select tissues to help regulate important functions such as:
- Appetite
- Digestion
- Immune function
- Inflammatory cascade, including neuroinflammation
- Mood
- Sleep
- Reproduction/fertility
- Motor control
- Temperature regulation
- Memory
- Discomfort
- Pleasure/reward
Your ECS has incredible precision
Once the endocannabinoids have done their job and brought things into balance, enzymes come along to break them down and prevent them from going too far and upsetting the balance in the opposite direction. The ECS has a very precise response, unlike using marijuana products with THC which floods your systems with cannabinoids that can have a wide-range of impacts on your physiology, some of which may be beneficial while others may be harmful.
Your body does produce an endocannabinoid similar to THC called anandamide, however you don’t experience the high like you do with THC. Anandamide does have a calming effect, though. In fact, it gets its name from ananda, the Sanskrit word for bliss.
A plant-based cannabinoid that's gotten a lot of attention from researchers is cannabidiol or CBD. It doesn't have any psychoactive properties, so its benefits come without the high of THC. One known function of CBD in the brain is to stop the enzymes from breaking down anandamide, so the anandamide can have more of an impact. That's believed to be why CBD can help treat feelings of anxiousness.
As we learn more about the endocannabinoid system, we are learning that you can have clinical endocannabinoid deficiency (CECD). CECD isn't a disease itself but is an umbrella term encompassing conditions that can include gestational issues, severe headaches, and chronic disorders characterized by widespread discomfort that is often accompanied by fatigue, low mood, sleep disturbance, cognitive impairment, and digestive and urinary symptoms.
Overall, ECS is a fascinating and incredibly important part of our eco-system that we want to ensure stays in balance.
References:
- Raypole, Crystal, “A Simple Guide to the Endocannabinoid System”, healthline, 17 May 2019, accessed 17 August 2020, < https://www.healthline.com/health/endocannabinoid-system>
- “The Endocannabinoid System”, Om of Medicine, accessed 17 August 2020, <https://www.omofmedicine.org/endocannabinoid-system/>
- Dellwo, Adrienne, “What is the Endocannabinoid System?”, verywell health, 10 February 2020, accessed on 17 August 2020, < https://www.verywellhealth.com/what-is-the-endocannabinoid-system-4171855>
